True Apparent Leg Length Discrepancy
Overview
Many people don?t realise it, but one of their legs is longer (or shorter) than the other one. Over time, this can lead to degenerative osteoarthritis (OA) in the hip joint requiring a hip replacement. But the surgeon can?t just take the old hip joint out and put the new implant in. Careful planning, special surgical techniques, and adjusting of the implant component parts are important in preventing continuation or even worsening of the leg length discrepancy.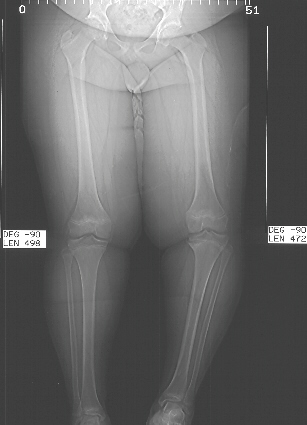
Causes
LLDs are very common. Sometimes the cause isn?t known. But the known causes of LLD in children include, injury or infection that slows growth of one leg bone. Injury to the growth plate (a soft part of a long bone that allows the bone to grow). Growth plate injury can slow bone growth in that leg. Fracture to a leg bone that causes overgrowth of the bone as it heals. A congenital (present at birth) problem (one whole side of the child?s body may be larger than the other side). Conditions that affect muscles and nerves, such as polio.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints.
Non Surgical Treatment
Internal heel lifts: Putting a simple heel lift inside the shoe or onto a foot orthotic has the advantage of being transferable to many pairs of shoes. It is also aesthetically more pleasing as the lift remains hidden from view. However, there is a limit as to how high the lift can be before affecting shoe fit. Dress shoes will usually only accommodate small lifts (1/8"1/4") before the heel starts to piston out of the shoe. Sneakers and workboots may allow higher lifts, e.g., up to 1/2", before heel slippage problems arise. External heel lifts: If a lift of greater than 1/2" is required, you should consider adding to the outsole of the shoe. In this way, the shoe fit remains good. Although some patients may worry about the cosmetics of the shoe, it does ensure better overall function. Nowadays with the development of synthetic foams and crepes, such lifts do not have to be as heavy as the cork buildups of the past. External buildups are not transferable and they will wear down over time, so the patient will need to be vigilant in having them repaired. On ladies' high-heel shoes, it may be possible to lower one heel and thereby correct the imbalance.

can gym help in increasing height?
Surgical Treatment
Shortening techniques can be used after skeletal maturity to achieve leg length equality. Shortening can be done in the proximal femur using a blade plate or hip screw, in the mid-diaphysis of the femur using a closed intramedullary (IM) technique, or in the tibia. Shortening is an accurate technique and involves a much shorter convalescence than lengthening techniques. Quadriceps weakness may occur with femoral shortenings, especially if a mid-diaphyseal shortening of greater than 10% is done. If the femoral shortening is done proximally, no significant weakness should result. Tibial shortening can be done, but there may be a residual bulkiness to the leg, and risks of nonunion and compartment syndrome are higher. If a tibial shortening is done, shortening over an IM nail and prophylactic compartment release are recommended. We limit the use of shortenings to 4 to 5 cm leg length inequality in patients who are skeletally mature.
Many people don?t realise it, but one of their legs is longer (or shorter) than the other one. Over time, this can lead to degenerative osteoarthritis (OA) in the hip joint requiring a hip replacement. But the surgeon can?t just take the old hip joint out and put the new implant in. Careful planning, special surgical techniques, and adjusting of the implant component parts are important in preventing continuation or even worsening of the leg length discrepancy.

Causes
LLDs are very common. Sometimes the cause isn?t known. But the known causes of LLD in children include, injury or infection that slows growth of one leg bone. Injury to the growth plate (a soft part of a long bone that allows the bone to grow). Growth plate injury can slow bone growth in that leg. Fracture to a leg bone that causes overgrowth of the bone as it heals. A congenital (present at birth) problem (one whole side of the child?s body may be larger than the other side). Conditions that affect muscles and nerves, such as polio.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints.
Non Surgical Treatment
Internal heel lifts: Putting a simple heel lift inside the shoe or onto a foot orthotic has the advantage of being transferable to many pairs of shoes. It is also aesthetically more pleasing as the lift remains hidden from view. However, there is a limit as to how high the lift can be before affecting shoe fit. Dress shoes will usually only accommodate small lifts (1/8"1/4") before the heel starts to piston out of the shoe. Sneakers and workboots may allow higher lifts, e.g., up to 1/2", before heel slippage problems arise. External heel lifts: If a lift of greater than 1/2" is required, you should consider adding to the outsole of the shoe. In this way, the shoe fit remains good. Although some patients may worry about the cosmetics of the shoe, it does ensure better overall function. Nowadays with the development of synthetic foams and crepes, such lifts do not have to be as heavy as the cork buildups of the past. External buildups are not transferable and they will wear down over time, so the patient will need to be vigilant in having them repaired. On ladies' high-heel shoes, it may be possible to lower one heel and thereby correct the imbalance.

can gym help in increasing height?
Surgical Treatment
Shortening techniques can be used after skeletal maturity to achieve leg length equality. Shortening can be done in the proximal femur using a blade plate or hip screw, in the mid-diaphysis of the femur using a closed intramedullary (IM) technique, or in the tibia. Shortening is an accurate technique and involves a much shorter convalescence than lengthening techniques. Quadriceps weakness may occur with femoral shortenings, especially if a mid-diaphyseal shortening of greater than 10% is done. If the femoral shortening is done proximally, no significant weakness should result. Tibial shortening can be done, but there may be a residual bulkiness to the leg, and risks of nonunion and compartment syndrome are higher. If a tibial shortening is done, shortening over an IM nail and prophylactic compartment release are recommended. We limit the use of shortenings to 4 to 5 cm leg length inequality in patients who are skeletally mature.